Backend Questions
Soft delete
By default, generated methods executes hard delete.
To enable soft deletion you only need to add an attribute to your model.
// File: DBModelsEx/CoreCompany.cs
using CoreType.Attributes;
[SoftDelete(nameof(Status), (int) Types.Status.Deleted)]
public partial class CoreCompany
{
// public int Status { get; set; } // Inherited from other partial class.
}
SoftDeleteAttribute
When this attribute is used on models, our context automatically filters out soft deleted records on select queries. On delete updates the record by specified property and value pair.
Arguments
- PropertyName : Name of property that manages soft deletion. Must be exactly same with your model's property.
- Value : Value to be assigned on soft deletion. Can be an enum or hardcoded value but type must be same with property's type.
Note: When attribute is defined, default delete behaviour changes to soft delete. But you can still call HardDelete to physically delete a record.
Forcing hard deletion from a repository:
public bool AnyMethod(SampleModelClass entity)
{
return HardDelete(entity);
}
Sending email and SMS
Instead of lots of coding, we recommend using communication middleware via Management / Communication
Resource code and Action for authorization
Please check all details in Authentication & Authorization
Logging
There exists a comprehensive logging middleware. Please check all details in Logging Middleware
Exclude a model/class property from logging
By adding [IgnoreLogging], [MaskedLogging] and [HashedLogging] attributes to model classes, you can manage logging for specific cases.
public class User
{
[IgnoreLogging] // Do not log "password" ever
[Column("password")]
public string Password { get; set; }
[MaskedLogging(@"\w\w(.*)\w")] // Log the value of "ibanNumber" as masked
[Column("ibanNumber")]
public string IbanNumber { get; set; }
[HashedLogging] // Log the value of "email" as hashed
[Column("email")]
public string Email { get; set; }
}
Please check all details in Logging Middleware
Base classes
Through base classes you can manage main classes in a centralized manner.
- Controllers implements
BaseController - Services implements
GenericService - Repositories implements
GenesisRepository - Models implements
BaseContract - Validators implements
AbstractValidator - DBContexts implements
ContextBase
Generic response object
There is a standard and generic reponse object returned for any method call.
| Property | Type |
|---|---|
| success | bool |
| message | string |
| errors | List<IHttpResponseException> |
| data | dynamic |
Example:
{
"success": false,
"message": "Something went wrong",
"errors": [
{
"code": "1020",
"message": "fullName cannot be null",
"stackTrace": "<Stacktrace of exception>"
}
],
"data": {}
}
EF Core performance
One of the most common pieces of advice is to use method called .AsNoTracking(). Supposedly this method greatly improves performance on EF queries.
Exception Handling
You don't need to handle exceptions in most of the time. Solution adds exception handling middleware, so you get nicely formatted exceptions. Check Exception Handling for more.
Caching
We use Redis caching but you can use in-memory interchangeably with a slight effort. Check Distributed Cache for more.
Enable Elastic Stack
Check Elastic Stack for further information.
Extension methods for EF Core in repository
AddFilters, AddSortings, AddPagination, AddFiltersAndPagination, SelectExclusively, ToPaginatedList and so on
TODO: will be elaborated.
Bulk/Batch transaction
If you create your project via AutoCode Solution Generator, you'll get BulkSave method for all of your controllers. If you upload/import an excel file from UI, it'll be handled automatically.
Thus, you won't need to struggle with tasks, threads, performance issues and so on.
If you go through boilerplate, you can find a sample in
CoreSvc/Controllers/UserController.cs
[HttpPost]
[ClaimRequirement(ActionType.Import)]
public ResponseWrapper BulkSave([FromBody] RequestWithExcelData<SampleModelClass> request)
{
return _mainService.BulkSaveAsync(request);
}
Override some columns/properties' values before writing to DB
Almost all Genesis models are inherited from GenesisBaseContract, which has 5 properties named CreatedUserId, CreatedDate, UpdatedUserId, UpdatedDate and TenantId. They are handled automatically by overriding EF Core context's SaveChanges method on ContextBase.
So you can use the same methodology by overriding your context's SaveChanges method. A sample code block is below:
public override int SaveChanges()
{
var entries = ChangeTracker.Entries()
.Where(entry => entry.State != EntityState.Unchanged)
.ToList();
foreach (var entry in entries)
{
// Check your entity type or interface to ensure those properties exsits
if (entry.State == EntityState.Added)
{
entry.CurrentValues["CreatedUserId"] = Session.CurrentUser.UserId;
entry.CurrentValues["CreatedDate"] = DateTime.UtcNow;
}
else if (entry.State == EntityState.Modified)
{
entry.CurrentValues["UpdatedUserId"] = Session.CurrentUser.UserId;
entry.CurrentValues[("UpdatedDate"] = DateTime.UtcNow;
}
}
return base.SaveChanges();
}
How model validation works?
We use FluentValidation which is a strong library to adapt and use easily.
As long as you include validator type to GenericRepository as generic argument, Save methods will validate entity before any database operations, you don't need to do it manually.
// Sample repository with auto validation.
public class SampleRepository : GenericRepository<SampleModelClass, int, SampleValidator>
{
// Save methods validates entity with "SampleValidator" before any database operation.
}
If you don't want this behaviour as default you can omit that generic argument and call Validate methods by yourself.
// Sample repository with manuel validation.
public class SampleRepository : GenericRepository<SampleModelClass, int>
{
public void AnyMethod(SampleModelClass entity)
{
ValidateAndThrow<SampleModelValidator>(entity);
// Same as below but overriding is possible with this way.
// new SampleModelValidator().ValidateAndThrow(entity);
...
}
}
Please visit FluentValidation official web site for details.
Set custom multi-language message for a specific control in Validator
...
RuleFor(x => x.TenantType) // Only SystemOwner can assign a new SystemOwner
.NotEqual(x => (int) TenantType.SystemOwner)
.When(x => SessionAccessor.GetSession().CurrentUser.TenantType != (int)TenantType.SystemOwner)
.WithMessage(session => DistributedCache.Get("YOU_CANNOT_ASSIGN_SYSTEM_OWNER_TENANTTYPE_MESSAGE")); // This line provides multi-language message
...
CORS-Origin settings
AllowedCorsOrigins setting is used to allow access for cross-origin requests. This is also be needed if you host your React UI or Microservices in separate servers/domains/ports.
Find coresettings.Development.json and coresettings.Production.json files. Ensure all your microservices those communicates with each other are added here.
{
...
"AllowedCorsOrigins": [
"http://localhost:3000",
"http://localhost:5050",
"http://localhost:5000"
],
...
}
Consider adding your domain addresses instead of localhost on non-development environments.
For more app settings, check Configuration.
How to manage and save FILE_UPLOADER's JSON data
By default, posted data for upload components is a json as:
{
"file": "iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAvQAAAISCAYAAACjwVuJAAAgAElEQVR4AeydB5wURfbHf70zG4jiAgossCxZghIERVhJBlDgwHAG1EPgCHreX4mCIlFFghhJCnIIKueJqCgiSthFgpJUctolr2Qkbpr....",
"fileName":"someImageName.png",
"mimeType":"image/png"
}
In that case, you should add a serializer to public partial class YourDBContextEx which is in YourMicroserviceName.DataLib
using CoreType.Types;
...
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
modelBuilder.Entity<SampleModelClass>(entity =>
{
entity.Property(e => e.YourFilesColumnName) // Don't forget to change YourFilesColumnName's type to FileContent in DataLib/DBModels/SampleModelClass.cs
.HasColumnName("<YourFilesColumnName>")
.HasColumnType("json") // If json is not supported you can use any varchar varient types.
.HasConversion(
v => JsonConvert.SerializeObject(v),
v => JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<FileContent>(v));
});
}
In DB, you don't need to use BLOB types. If your preferred DB supports JSON data-type (as for PostgreSQL), use it. Otherwise, we recommend
nvarchar(max)ortext.
Can we choose different DBs for each microservice throughout AutoCode Solution Generation?
Yes, you can specify MSSQL Server for first microservice and PostgreSQL for the other one. It is flexible to choose amongst DB servers, schemas or tables for different microservices.
Throw a custom multi-language error message
LocalizedMessages class is a life saver for dealing with localizations. It localizes and caches all messages by a specified locale or even by requested locale from your UI. It can be used on everywhere including for exceptions.
throw new GenesisException(LocalizedMessages.RESET_PASSWORD_EXPIRED);
If you want to set dynamic variable into the message
// "Message includes variables as {0} and {1}"
throw new GenesisException(LocalizedMessages.ANY_MESSAGE_WITH_ARGS, SomeVariable1, SomeVariable2);
What happens if I use Where condition and AddFilters, AddFiltersAndPagination extension methods together?
No problem. Conditions will be added to each other with "AND" operand with a natural way.
public override async Task<PaginationWrapper<SampleModelClass>> ListAsync(RequestWithPagination<SampleModelClass> request)
{
var query = DbSet(noTracking: true);
if (Session.CurrentUser.TenantType == (int) TenantType.SystemOwner)
query = query.IgnoreQueryFilters();
if (request.Criteria.ExcludeStatus != null)
query = query.Where(x => x.Status != request.Criteria.ExcludeStatus);
return query.AddFilters(request)
.OrderBy(x => x.Status)
.ToPaginatedList(request);
}
How should I proceed to use Model-First/Code-First approach?
You can benefit AutoCode Solution Generator's update method.
Check on Genesis Migration
Encrypt-Decrypt method
Find sample in CommunicationManager.cs
string encryptedPassword = EncryptionManager.Encrypt(somePassword);
string decryptedPassword = EncryptionManager.Decrypt(encryptedPassword);
EncryptionManager's methods uses symmetric key provided from coresettings files. This key is uniquely generated on Solution Generation. Each environment can have different keys to separate encrypted data algorithm.
{
...
"Encryption": {
"SymmetricKey": "<guid>"
}
...
}
Can I use ToPaginatedList and AddPagination extension methods together?
No need and you should NOT use them together which could end up with multiple offsetted result set.
Store/persist data as encrypted but decrypt it when fetched
using CoreType.Attributes;
namespace Microservice.DataLib.DBModels
{
public partial class SampleModelClass
{
...
[HashedLogging] // Log the password as hashed
public string Password { get; set; }
[EncryptedPersistence] // Store the gender as encrypted since it is subject to GDPR
[IgnoreLogging] // Don't log the gender
public short? Gender { get; set; }
[HashedPersistence] // Stora data as hashed
[HashedLogging] // Log as hashed
public string SomeHashValue { get; set; }
....
}
}
How can I view methods to override in Service and Repository layers?
Depending on your development IDE, right click Quick actions and refactorings -> Generate overrides -> Choose the methods
| Quick actions and refactorings | Generate overrides | Choose the methods |
|---|---|---|
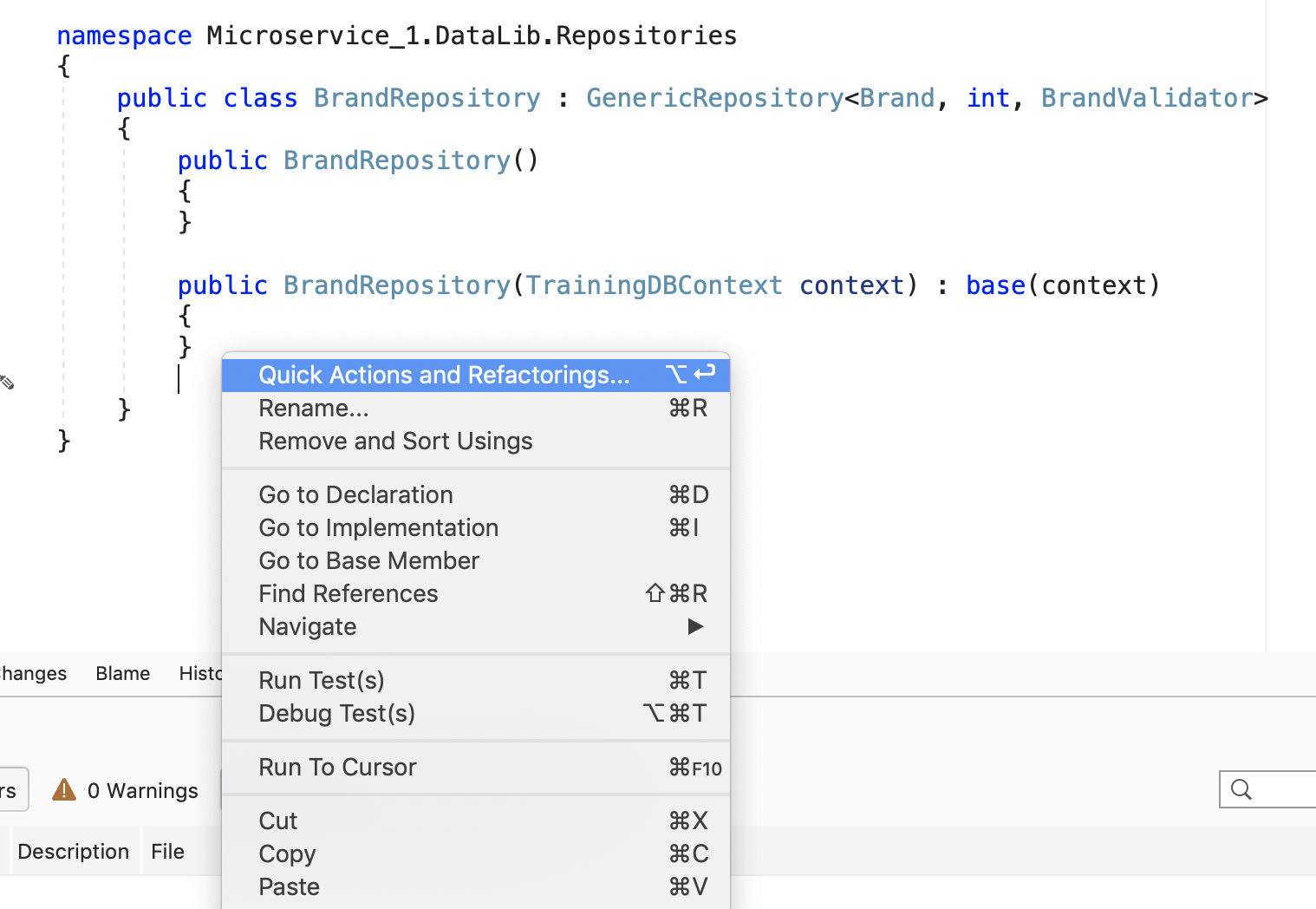 | 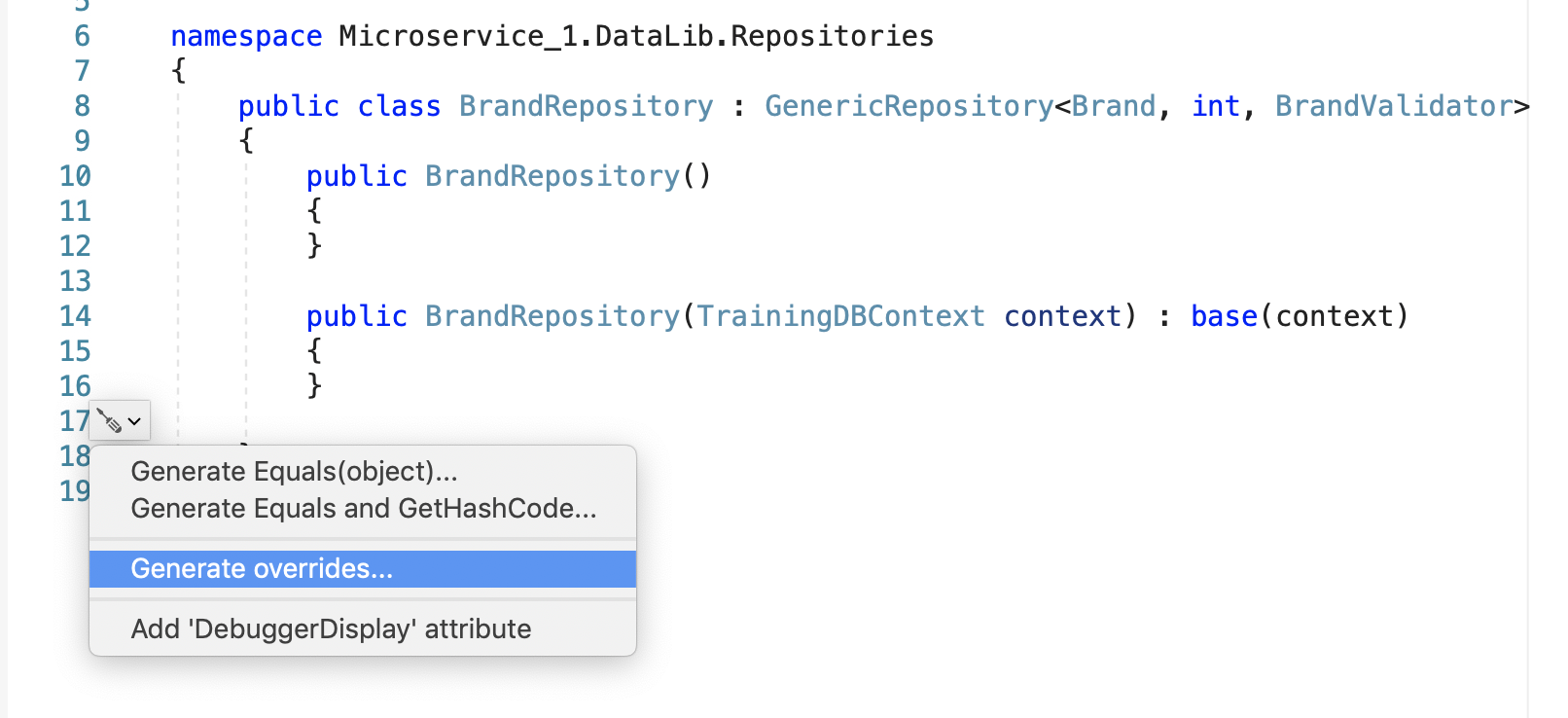 | 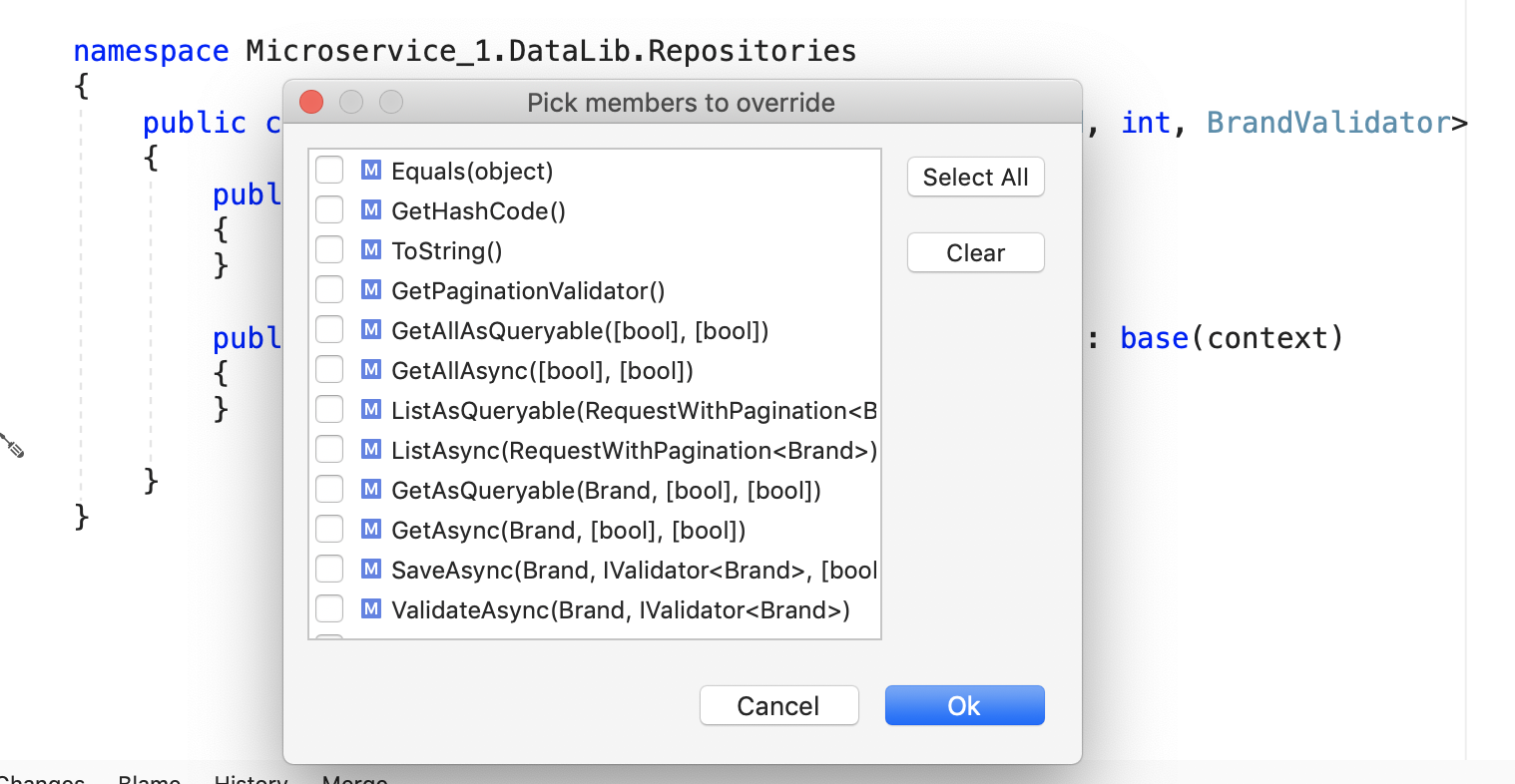 |
Check
Base.CoreData.Repositories.UserRepository.csfor a sample
TODOs
Scheduling Monitoring
Add new controller
Change IdentityServer
Integrate to Active Directory or LDAP
Extended partial classes
DBContextEx and DBModelEx
Swagger as documentation
Dependency injection
DTOs
Object AutoMapper
Unit testing
Extending Existing Entities
SignalR integration
Notification sending
Login process
hashed password, call sp, validate and get claims